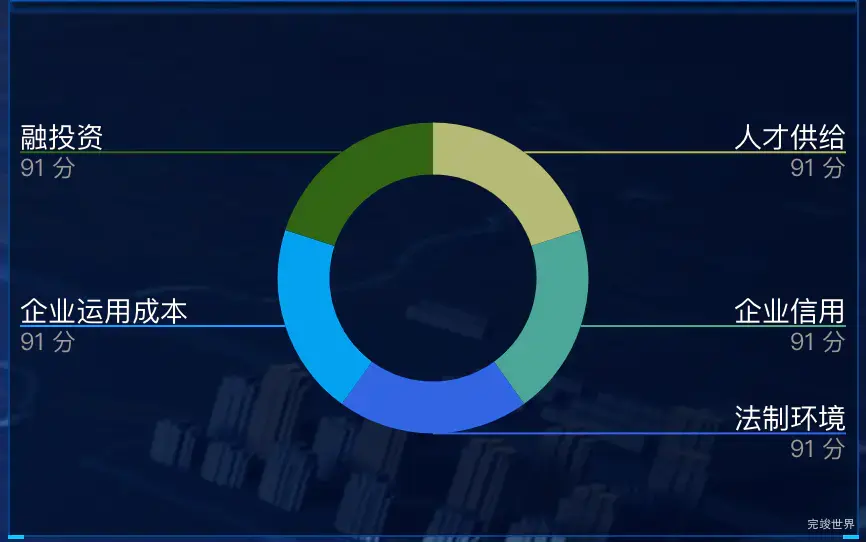
数据可视化大屏项目开发中,为了增加大屏样式的多元化,会设置各种各样的样式,今天要实现的效果样式是label分为两行,引导线从label两行文字中间穿过。
echarts版本
"echarts": "^5.2.0",
关键代码
label: {
alignTo: 'edge',
formatter: '{name|{b}}\n{time|{c} 分}',
minMargin: 5,
edgeDistance: 5,
lineHeight: 15,
rich: {
name: {
color: '#FFF', // 白色字体
fontSize: 14, // 14号字体
},
time: {
fontSize: 12, // 字号改为14
color: '#999' // 灰色字体
}
}
},
labelLayout: function (params) {
const isLeft = params.labelRect.x < myChart.getWidth() / 2;
const points = params.labelLinePoints;
// Update the end point.
points[2][0] = isLeft
? params.labelRect.x
: params.labelRect.x + params.labelRect.width;
return {
labelLinePoints: points
};
},
参数介绍
alignTo
标签的对齐方式,仅当 position 值为 'outer' 时有效。
从 ECharts v4.6.0 版本起,我们提供了 'labelLine' 与 'edge' 两种新的布局方式。
'none'(默认值):label line 的长度为固定值,分别为 labelLine.length 及 labelLine.length2。
'labelLine':label line 的末端对齐,其中最短的长度由 labelLine.length2 决定。
'edge':文字对齐,文字的边距由 label.edgeDistance 决定。
labelLayout
从 v5.0.0 开始支持
标签的统一布局配置。
该配置项是在每个系列默认的标签布局基础上,统一调整标签的(x, y)位置,标签对齐等属性以实现想要的标签布局效果。
该配置项也可以是一个有如下参数的回调函数
// 标签对应数据的 dataIndex
dataIndex: number
// 标签对应的数据类型,只在关系图中会有 node 和 edge 数据类型的区分
dataType?: string
// 标签对应的系列的 index
seriesIndex: number
// 标签显示的文本
text: string
// 默认的标签的包围盒,由系列默认的标签布局决定
labelRect: {x: number, y: number, width: number, height: number}
// 默认的标签水平对齐
align: 'left' | 'center' | 'right'
// 默认的标签垂直对齐
verticalAlign: 'top' | 'middle' | 'bottom'
// 标签所对应的数据图形的包围盒,可用于定位标签位置
rect: {x: number, y: number, width: number, height: number}
// 默认引导线的位置,目前只有饼图(pie)和漏斗图(funnel)有默认标签位置
// 如果没有该值则为 null
labelLinePoints?: number[][]
完整实例代码
drawLine() {
// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例
window.addEventListener('resize', this.drawLine)
const myChart = echarts.init(this.$refs.echarts)
var option = {
tooltip: {
trigger: 'item',
},
color: ['#b5ba76', '#4ca698', '#3165e3', '#05a1ef', '#316513'],
grid: {
left: 10,
top: 50,
bottom: 10,
right: 10,
containLabel: true
},
polar: {},
angleAxis: {
interval: 1,
type: 'category',
data: [],
z: 10,
axisLine: {
show: false,
lineStyle: {
color: '#10417d',
width: 1,
type: 'solid'
}
},
axisLabel: {
interval: 0,
show: true,
color: '#10417d',
margin: 8,
fontSize: 16
}
},
radiusAxis: {
min: 40,
max: 120,
interval: 20,
axisLine: {
show: false,
lineStyle: {
color: '#10417d',
width: 1,
type: 'solid'
}
},
axisLabel: {
formatter: '{value} %',
show: false,
padding: [0, 0, 20, 0],
color: '#10417d',
fontSize: 16
},
axisTick: { // y轴刻度线
show: false
},
splitLine: {
show: false,
lineStyle: {
color: '#10417d',
width: 2,
type: 'solid'
}
}
},
calculable: true,
series: [
{
type: 'pie',
center: ['50%', '50%'],
radius: ['40%', '60%'],
label: {
alignTo: 'edge',
formatter: '{name|{b}}\n{time|{c} 分}',
minMargin: 5,
edgeDistance: 5,
lineHeight: 15,
rich: {
name: {
color: '#FFF', // 白色字体
fontSize: 14, // 14号字体
},
time: {
fontSize: 12, // 字号改为14
color: '#999' // 灰色字体
}
}
},
labelLayout: function (params) {
const isLeft = params.labelRect.x < myChart.getWidth() / 2;
const points = params.labelLinePoints;
// Update the end point.
points[2][0] = isLeft
? params.labelRect.x
: params.labelRect.x + params.labelRect.width;
return {
labelLinePoints: points
};
},
data: this.list
}
]
}
myChart.clear()
myChart.resize()
myChart.setOption(option)
}